Building on exploration success at flagship Matagami project
Nuvau Minerals Inc. (TSXV: NMC,OTC:NMCPF) is pleased to provide a corporate update, highlighting the success of 2025 exploration programs and plans for 2026. Previous exploration has resulted in significant gold and base metal discoveries and has expanded the Company’s base metal mineralized inventory at its Matagami Project in the Abitibi region of Québec.
‘We went public in late 2024 with a mandate to increase base metal resources, initiate gold-focused exploration that has been overlooked on our large-scale property, and accelerate work toward restarting mining operations,’ said Peter van Alphen, Nuvau’s President and Chief Executive Officer. ‘With extensive existing processing and permitted mining operations, the Matagami Property truly represents a near-term production opportunity with limited start-up capital. We have made significant progress, developing two zones of volcanogenic massive sulphide (VMS) mineralization, discovering a new orogenic gold system at Bracemac, and expanding mineralization at the Bracemac-McLeod Mine. This work sets the groundwork for an updated mineral resource estimate on the property, updated economic studies, and advancing the completion of the earn-in from Glencore.’
Key achievements in 2025
Exploration continued across the property, while also progressing multiple initiatives aimed at advancing the planned restart of production:
- A sonic drilling program was completed to explore for mineralization in the glacial till, which delivered a significant gold grain anomaly with more than 2,000 gold grains per 10 kg of material, in an underexplored part of the property, supported by a near-contiguous sample with 295 gold grains, in hole PD-23-030s.
- Caber Complex Base Metal Project – The company completed a successful drilling program that returned numerous high-grade intercepts at the Caber Complex deposit. This work was completed to increase drill density in preparation for the completion of an updated Mineral Resource Estimate (MRE).
- Renaissance Zone – Following the 2023 new VMS discovery, from the first geophysical target tested by Nuvau to the north of the Caber deposits. Twenty-seven holes were drilled, with 16 holes containing semi-massive to massive sulphide mineralization. Additional VMS mineralization was discovered at the PD1-East target, a nearby geophysical anomaly tested in 2025.
- McLeod Extension – Seven new intersections from 5,526 metres of drilling in 2024 and 2025, following up on the 2023 program that discovered potential to expand mineralization proximal to existing mine workings, including an impressive intercept of 15.30 metres grading 2.92% copper, 15.32% zinc, 0.39 g/t gold, and 98.16 g/t silver.
A new prospective gold horizon was discovered in 2025, immediately east of the Bracemac Mine within a Tonalite intrusive, where the very first drill hole intersected visible gold in quartz veining that returned 8.87 g/t gold over 1.05 metres, including 16.02 g/t gold over 0.55 (BRCG-25-01). Follow-up drilling confirmed continuity of a broad, near-surface mineralized system within a large-scale target area, not tested in historic programs. Assay results are provided in Table 1 and 2 at the end of the document.
Strategic focus in 2026
The Matagami camp uniquely combines district-scale exploration potential with a near-term production restart opportunity, supported by a large land package, existing mineral endowment, and permitted infrastructure. Figure 1 highlights some of the priority exploration target areas.
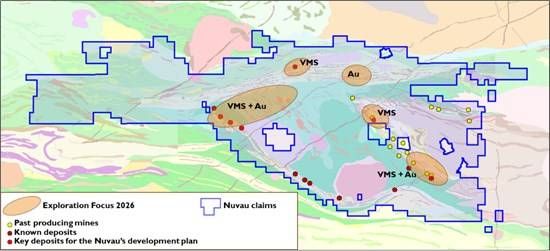
Figure 1: Nuvau’s 2026 exploration focus areas for gold and base metals (volcanogenic massive sulfides)
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
https://images.newsfilecorp.com/files/11236/282093_dcb70e799442ea69_001full.jpg
The company is preparing for a large-scale exploration program in 2026, continuing to test multiple high-quality gold targets and several promising base metal targets, including the Daniel 25 VMS area and untested geophysical anomalies in the central camp.
Gold exploration will focus on the underexplored area hosting the high-grade gold-in-till anomaly, advancing the Thunder Mine target where historic drilling intersected multiple high-grade zones that remain open, and evaluating the broader prospectivity of the footwall gold occurrence at the Bracemac Mine. All permits have been received for the expected exploration program for 2026.
Nuvau will continue to advance work aimed at updating its Mineral Resource Estimates for the multiple deposits located on the property, targeting upgrades to the Caber Complex, as well as initial mineral resource estimates for Bracemac-McLeod and Renaissance.
Following the resource updates, the company anticipates updating the previously completed PEA to include portions of those additional resources, as well as updating the associated economics and mine plans. Permitting initiatives will also continue to prepare the Matagami Property for the restart of mining operations.
Update on Matagami earn-in
Nuvau continues to advance its earn-in with respect to the Matagami Property. On January 28, 2026, Nuvau, Nuvau Minerals Corp. and Glencore Canada Corporation (‘Glencore’) entered into a second amended and restated earn-in agreement (the ‘Second A&R Earn-In Agreement’), which further amends and restates the terms of the earn-in agreement dated March 25, 2022, as previously amended and restated on June 28, 2024.
As Nuvau has satisfied all work requirements to earn the right to acquire a 100% interest in the Matagami Property, Nuvau has been working closely with Glencore to complete the transfer of Glencore’s interest in the Matagami Property to Nuvau. In order to facilitate such transfer, Nuvau and Glencore have agreed to certain technical amendments in the Second A&R Earn-In Agreement to address, among other things, certain regulatory considerations, the obligations of Nuvau with respect to the replacement of financial assurances, and the transfer of permits and authorizations to Nuvau. In addition, Nuvau also agreed to guarantee certain deferred obligations under the Second A&R Earn-In Agreement, updated to reflect status of Nuvau Minerals Inc. as guarantor of the obligations. Pursuant to the Second A&R Earn-In Agreement, Nuvau must complete the earn-in by no later than February 27, 2026.
For additional information, please refer to the Second A&R Earn-In Agreement, a copy of which will be available on SEDAR+ (www.sedarplus.ca) under Nuvau’s issuer profile.
Table 1: Bracemac gold showing assay intervals
| DDH interval* |
From |
To |
Length |
Gold g/t |
| BRCG-25-01 |
255.75 |
265.00 |
9.25 |
1.13 |
| Including |
255.75 |
256.80 |
1.05 |
8.87 |
| BRCG-25-02 |
273.60 |
274.10 |
0.50 |
7.07 |
| BRCG-25-03 |
187.20 |
195.40 |
8.20 |
0.20 |
| Including |
187.20 |
188.00 |
0.80 |
1.37 |
| BRCG-25-04 |
96.25 |
96.75 |
0.50 |
1.17 |
| BRCG-25-04 |
196.80 |
233.40 |
36.6 |
0.40 |
| Including |
196.80 |
197.30 |
0.50 |
7.61 |
| Including |
202.30 |
202.85 |
0.55 |
3.15 |
| Including |
228.00 |
229.00 |
1.00 |
4.27 |
| BRCG-25-04 |
293.70 |
294.20 |
0.50 |
2.23 |
| BRCG-25-05 |
100.00 |
100.75 |
0.75 |
1.98 |
| BRCG-25-05 |
394.10 |
401.30 |
7.20 |
0.30 |
| Including |
394.10 |
394.90 |
0.80 |
1.35 |
| Including |
400.80 |
401.30 |
0.50 |
1.54 |
* Intervals conveying more than 1 g/t of gold or more than 5 m of composites > 0.2 g/t gold.
* All lengths are core lengths; true width is unknown.
Table 2: Bracemac gold DDH collar position (NAD83/UTM zone18) and drilling direction
| DDH |
X |
Y |
Az. |
Dip. |
| BRCG-25-01 |
307638 |
5506552 |
179.1 |
64.5 |
| BRCG-25-02 |
307638 |
5506552 |
170.9 |
63.4 |
| BRCG-25-03 |
307638 |
5506552 |
177.6 |
57.6 |
| BRCG-25-04 |
307690 |
5506630 |
200.5 |
51.3 |
| BRCG-25-05 |
307690 |
5506630 |
196.6 |
66.2 |
About Nuvau Minerals Inc.
Nuvau is a Canadian mining company focused on the Abitibi Region of mine-friendly Québec. Nuvau’s principal asset is the Matagami Property that is host to significant existing processing infrastructure and multiple mineral deposits and is being acquired from Glencore.
For further information, please contact:
Nuvau Minerals Inc.
Peter van Alphen
President and CEO
Telephone: 416-525-6023
Email: pvanalphen@nuvauminerals.com
Qualified Person and Quality Assurance
Bastien Fresia P. Geo. (Qc), Technical Services Director of Nuvau and a ‘qualified person’ as is defined by National Instrument 43-101, has verified the scientific and technical data disclosed in this news release, and has otherwise reviewed and approved the scientific and technical information in this news release.
Sonic Core has been quicklogged on drilling site and shipped by truck to IOS facilities in Saguenay for detailed logging and sampling by a qualitifed quartenary geologist. Hole core from selected intervals has been bagged and queued for processing in the same facility, where samples were sifted and gold grain concentrated with a proprietary fluidized bed. Concentrates were then dry sifted at 50 μm, the +50 μm being examined under an optical microscope, while the -50 μm was scanned by an automated electron microscope. Every suspected gold grain has been analyzed by Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectrometer (EDS), and high magnification back-scattered images have been acquired in order to classify morphology. Quality control is ensured via various mass balance calculations and EDS analysis of all grains of interest, prior to results being cross-examined by experienced geologists. In the course of sifting, an aliquot of the sample has been saved and shipped for analysis to Activation Laboratories in Ancaster, Ontario, for ICP-MS-QQQ ultra-trace analyses after aqua-regia digestion. Quality control has been conducted by a certified chemist and includes approximately 15% blanks, certified reference materials and internal reference materials.
Diamond Drill core samples are sawn by staff technicians in Nuvau’s Matagami’s core shed to create half-core splits. One split is retained in the drill core box for archival purposes with a sample tag affixed at each sample interval, and the other split is placed in a labelled plastic bag along with a corresponding sample number tag and placed in the shipment queue. Quality control samples, including blind certified reference material (‘CRM’), blank material, and core duplicates, are inserted at a frequency of 1 in every 20 samples and sample batches of up to 60 samples were then shipped directly by Nuvau personnel to the ALS Canada Ltd. preparation laboratory in Rouyn-Noranda, Québec. All submitted core samples are crushed in full to 95 % passing less than 2 mm (ALS code CRU-32). A 1000-gram sample was then riffled, split from the crushed material and pulverized to 90 % passing 75 μm (SPL-22 and PUL-32a). Pulps are shipped from the preparation laboratory to ALS Canada Ltd.’s analytical lab in North Vancouver, British Columbia, for assay. Lead, silver, copper and zinc analyses were determined by ore grade four acid digestion with an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (‘ICP-AES’) or atomic absorption spectroscopy (‘AAS’) finish (ALS codes Pb-OG62, Ag-OG62, Cu-OG62 and ZnOG62), whereas gold was determined by 50 g fire assay analysis with an AAS finish (code Au-AA23).
PhotonAssay analysis (code Au-PA01) is used on the samples from Bracemac Gold. The samples are sent to Val d’Or MSALabs. Up to 1kg per sample is pulverized to 70% passing 2mm (CRU-CPA), encapsulated in 500g capacity separated plastic lids, adapted for the method and identified with barcodes and unique ID numbers. The Gamma Ray-based Photon Assay is directly processed in the MSALabs Val d’Or facilities. As the method is non-destructive, the assays can be reprocessed and are conserved for archive and future use in the plastic lids. For comparison, at the initiation of the drilling campaign, the method was tested against Fire Assays in ALSLabs, a 50 g fire assay analysis returned 15.75 g/t Au, compared to 16.02 g/t Au by PhotonAssay.
Cautionary Statements
This news release contains forward-looking statements and forward-looking information (collectively, ‘forward-looking statements’) within the meaning of applicable securities laws. Any statements that are contained in this news release that are not statements of historical fact may be deemed to be forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements are often identified by terms such as ‘may’, ‘should’, ‘anticipate’, ‘will’, ‘estimates’, ‘believes’, ‘intends’ ‘expects’ and similar expressions which are intended to identify forward-looking statements. More particularly and without limitation, this news release contains forward-looking statements concerning drill results relating to the Matagami Property, the results of the PEA, the potential of the Matagami Property, the timing and commencement of any production, the restart of the Bracemac-McLeod Mine, the completion of the earn-in of the Matagami Property and the timing and completion of any technical studies, feasibility studies or economic analyses. Forward-looking statements are inherently uncertain, and the actual performance may be affected by a number of material factors, assumptions and expectations, many of which are beyond the control of the Company, including expectations and assumptions concerning the Company and the Matagami Property. Readers are cautioned that assumptions used in the preparation of any forward-looking statements may prove to be incorrect. Events or circumstances may cause actual results to differ materially from those predicted as a result of numerous known and unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors, many of which are beyond the control of the Company. Readers are further cautioned not to place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements, as such information, although considered reasonable by the management of the Company at the time of preparation, may prove to be incorrect and actual results may differ materially from those anticipated.
The forward-looking statements contained in this news release are made as of the date of this news release, and are expressly qualified by the foregoing cautionary statement. Except as expressly required by securities law, neither the Company nor Nuvau undertakes any obligation to update publicly or to revise any of the included forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
Neither the TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this news release. No stock exchange, securities commission or other regulatory authority has approved or disapproved the information contained herein.

To view the source version of this press release, please visit https://www.newsfilecorp.com/release/282093


















