Cassiar Gold Corp. (TSXV: GLDC,OTC:CGLCF) (OTCQX: CGLCF) (the ‘Company’) is pleased to announce results from nine initial diamond drill holes of the 2025 exploration program at the Taurus Deposit, which is located within the Cassiar Gold Project, in northern British Columbia. Results from these drill holes demonstrate potential for ongoing expansion of near-surface mineralization along key structural trends and increase the population of high-grade, visible gold-bearing veins at the deposit. The 2025 drill program comprised 7,308 meters (m) over 20 drill holes and concluded in early October. Results are pending for 5,243 m of drilling over 11 drill holes from the Newcoast regional prospect which lies 2 kilometers (km) to the south.
Highlights:
Drill holes from the Taurus deposit reported here encountered significant intercepts above the 0.4 grams per tonne (g/t) gold (Au) cutoff of the 2025 Mineral Resource at Taurus[1], with repeated occurrence of high-grade samples hosted within broader mineralized intervals. Results expand mineralization near surface and beyond the extent of the current resource block model.
Drilling intercepts are uncapped unless otherwise stated and represent apparent widths of mineralized zones. A full summary of the latest results can be found in Table 1, and include:
- Drill hole 25TA-245 encountered multiple quartz veins with visible gold, returning:
- 13.4 m of 13.4 g/t Au (2.05 g/t Au capped) from 28.2 m downhole in drill hole 25TA-245, including:
- 56.10 g/t Au over 0.3 m, and
- 210.71 g/t Au over 0.8 m, with 0.4 m of 369.00 g/t Au
- 13.4 m of 13.4 g/t Au (2.05 g/t Au capped) from 28.2 m downhole in drill hole 25TA-245, including:
- Drill hole 25TA-242:
- 21.9 m of 2.81 g/t Au (2.80 g/t Au capped) from 45.8 m downhole, including:
- 9.41 g/t Au over 1.5 m,
- 5.41 g/t Au over 2.7 m, and
- 6.90 g/t Au over 2.3 m, with 0.30 m of 20.30 g/t Au
- 21.9 m of 2.81 g/t Au (2.80 g/t Au capped) from 45.8 m downhole, including:
- Drill hole 25TA-238:
- 21.7 m of 1.30 g/t Au from 13.1 m down hole, including
- 8.1 m of 2.18 g/t Au and 0.9 m of 5.11 g/t Au
- 11.3 m of 1.21 g/t Au, including
- 0.6 m of 8.33 g/t Au, and 0.8 m of 7.38 g/t Au
- 0.9 m of 27.18 g/t Au (9.63 g/t Au capped), including 59.50 g/t Au
- 21.7 m of 1.30 g/t Au from 13.1 m down hole, including
- Drill hole 25TA-239:
- 7.56 g/t Au over 2.0 m, including 0.4 m of 19.55 g/t Au and 0.8 m of 9.14 g/t Au
‘Our exploration programs demonstrate the Cassiar Gold Project holds meaningful potential as a gold resource expansion opportunity in an important region in British Columbia,’ stated Marco Roque, President and Chief Executive Officer of Cassiar Gold. ‘Confirming continuity and establishing extensions of near-surface higher-grade mineralization in the Taurus East, Southwest, and Sable areas demonstrates that this well-established foundational resource can continue to grow.’
‘Our drilling continues to delineate and extend new higher-grade trends within and adjacent to the Taurus deposit,’ stated Jill Maxwell, VP Exploration of Cassiar Gold. ‘We continue to intersect visible gold in structures across the deposit, with opportunity to identify new trends and advance higher-grade domains along-strike and down-dip in future programs. The results from Taurus East are particularly encouraging as we continue to evaluate the emerging volume potential at recently established satellite zones in the resource area, within the footprint of the existing mine permit.’

Figure 1. Cassiar North 2025 drill campaign drill hole location plan map of expansion and exploration drilling at the Taurus deposit and Newcoast prospect, with locations of drill holes reported within this news release contained within the blue outline (shown in detail in Figure 4).
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
https://images.newsfilecorp.com/files/2958/276754_cassiar%20figure%201.jpg
Taurus Deposit
The Taurus Deposit hosts a recently updated substantial near-surface, bulk-tonnage gold resource comprising an Indicated Mineral Resource of 8.8 million tonnes at 1.43 g/t Au for 410,000 ounces; with an additional Inferred Mineral Resource of 63.2 million ounces at 0.95 g/t Au for 1.93 million ounces[1], which remains open for expansion. Mineralization outcrops in places, with 91% of the ounces in the resource occurring within 150 m of surface. Ongoing expansion of the deposit footprint and follow up to recently identified higher grades trends remained a priority during the 2025 exploration campaign. A total of nine drill holes were completed at the Taurus deposit this season.
2025 Taurus Drill Holes
The drilling results reported in this news release are from nine drill holes totaling 2,066 m which tested the outer margins of the known extents of the Taurus deposit. Drilling was distributed across a 1.3-kilometer corridor of the deposit footprint to evaluate the expansion potential of mineralization beyond the block model with step outs ranging from 30 m up to 110 m. The program also followed up to recently identified quartz veins hosting higher grade gold mineralization along key controlling structural trends (Figure 1). Several higher-grade sample intervals were intersected internal to broader mineralized intercepts (Table 1). These extend the distribution of near-surface mineralization south, east, and west of previous drilling along an extensive east-northeast striking corridor of sheeted extensional vein sets within an associated prospective, Au-bearing carbonate-pyrite alteration halo.
Taurus East: drill holes 25TA-243 through 25TA-246
Drill hole 25TA-245 (west-oriented), aimed to evaluate the potential to expand the footprint of the 2025 resource model toward surface through testing potential parallel veins and interpreted extensions of mineralized veining. Drill holes 25TA-243, -244, and -246 (northwest oriented) were designed to test the potential for parallel sets, as well as extensions of veins along-strike and down-dip to the east, west, and south beyond the extent of the 2025 block model.
All of these drill holes returned gold-mineralized intercepts, including 25TA-245 which encountered high grade samples with visible gold hosted within broader intervals. These drill holes collectively expand the footprint of known mineralization near-surface and along strike to the south, west, and east beyond the extend of the 2025 block model. Results include (Table 1; Figures 2,3,4):
- Drill hole 25TA-245 encountered multiple specks of visible gold, returning:
- 13.4 m of 13.53 g/t Au (2.05 g/t Au capped) from 28.2 m downhole, including
- 0.3 m of 56.10 g/t Au, and
- 0.8 m of 210.71 g/t Au with 0.4 m of 369.00 g/t Au,
- 13.4 m of 13.53 g/t Au (2.05 g/t Au capped) from 28.2 m downhole, including
- 27.3 m of 0.65 g/t Au from 88.4 m downhole, including 1.1 m of 4.42 g/t Au with 0.6 m of 6.01 g/t Au in hole 25TA-244, and
- 3.6 m of 1.48 g/t Au from 61.2 m downhole, including 0.5 m of 7.08 g/t Au in 25TA-243.

Figure 2. Vertical section of drill hole 25TA-245 at Taurus East, looking to the south. Assay results in red text, along with select higher grade nested intervals in black, are reported in this new release. Section width +/- 25 m. Location of section line A-A’ is shown in plan view Figure 4. See Table 1 for comprehensive assay highlights.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
https://images.newsfilecorp.com/files/2958/276754_cassiar%20figure%202.jpg

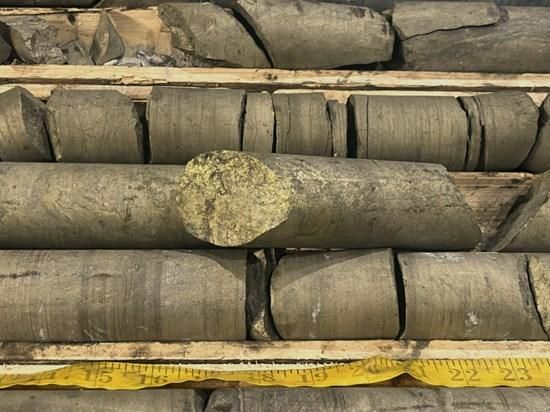
Figure 3. Visible gold in drill hole 25TA-245 observed in quartz veins hosted in Fe-carbonate-sericite altered and sulphide-mineralized basalt.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
https://images.newsfilecorp.com/files/2958/276754_cassiar%20figure%203.jpg
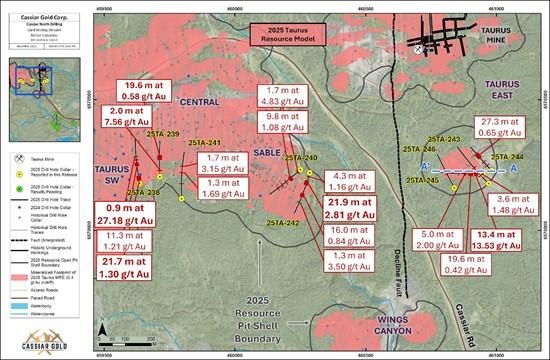
Figure 4. Plan view map of 2025 drill holes reported in this news release. The map location is shown in Figure 1. The vertical projection of mineralized intercepts reported in this release are included for reference, the blue dashed line denoted A – A’ represents the section line location for Figure 2.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
https://images.newsfilecorp.com/files/2958/276754_cassiar%20figure%204.jpg
Sable: drill holes 25TA-242, -240
Drill hole 25TA-242 (south-oriented) was designed to test an eastward extension of a higher-grade domain of mineralized quartz veining by evaluating the potential influence of an interpreted discrete northeast target plane previously untested at this locale. Drill hole 25TA-240 (southwest-oriented) aimed to test for down dip extensions of known mineralization at Sable.
Mineralization was encountered at the interpreted extensions of mineralized trends at Sable, beyond the extent of the current resource block model. Results include (Table 1; Figure 3):
- Multiple intercepts returned in hole 25TA-242:
- 21.9 m of 2.81 g/t Au (2.80 g/t Au capped) from 45.8 m downhole, including
- 1.5 m of 9.41 g/t Au, and
- 2.7 m of 5.41 g/t Au with 0.4 m of 8.01 g/t Au,
- also including 0.6 m of 7.35 g/t Au, and
- 2.3 m of 6.90 g/t Au with 0.3 m of 20.30 g/t Au;
- 16.0 m of 0.84 g/t Au from 123.0 m downhole, including 3.1 m of 2.72 g/t Au with 0.5 m of 6.12 g/t Au
- 21.9 m of 2.81 g/t Au (2.80 g/t Au capped) from 45.8 m downhole, including
- 9.8 m of 1.08 g/t Au from 70.5 m downhole, including 0.5 m of 6.79 g/t Au in hole 25TA-240
Taurus Southwest and Central: drill holes 25TA-238, -239, -241
Drill hole 25TA-238 and 25TA-239 (north-oriented) were designed as follow up to expansion holes from the 2024 drill program which encountered intervals of higher-grade mineralization and visible gold within broader intercepts, such as drill hole 24TA-236 with 184.50 g/t Au over 0.3 m nested in a broader intercept of 3.18 g/t Au over 21.9 m (see NEWS RELEASE, January 16, 2025), while 25TA-241 was designed to test for parallel vein sets to the south of the 2025 Taurus resource.
All drill holes from the Southwest and Central areas returned gold-mineralized intercepts, including 25TA-238 which encountered high grade mineralization with visible gold hosted within a broader interval. Results include (Table 1; Figure 4,5):
- Drill hole 25TA-238:
- 21.7 m of 1.30 g/t Au from 13.1 m downhole, including 8.1 m of 2.18 g/t Au and 0.9 m of 5.11 g/t Au
- 11.3 m of 1.21 g/t Au from 101.4 m downhole, including 0.6 m of 8.33 g/t Au and 0.8 m of 7.38 g/t Au
- 0.9 m of 27.18 g/t Au (9.63 g/t Au capped) from 148.9 m downhole, including 0.4 m of 59.50 g/t Au with visible gold
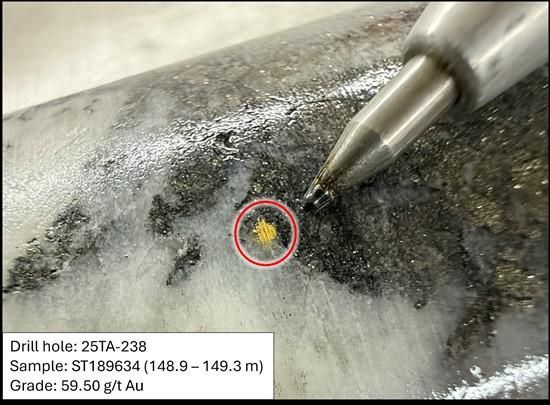

Figure 5. Visible gold in drill hole 25TA-238 observed in quartz veins hosted in Fe-carbonate-sericite altered and sulphide-mineralized basalt.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
https://images.newsfilecorp.com/files/2958/276754_cassiar%20figure%205.jpg
Summary
Drilling at the Taurus deposit continues to demonstrate potential for ongoing expansion of near-surface mineralization along the main east-northeast striking sheeted vein sets than defined by the 2025 mineral resource estimate. Drill holes reported here increase the population of high-grade, visible gold-bearing veins at the deposit, such as drill hole 25TA-245 which delivered 0.3 m grading 56.10 g/t Au and 0.4 m grading 369.00 g/t, and hole 25TA-238 with 59.50 g/t over 0.4 m, nested in broader intercepts (Table 1). The technical team continues to evaluate the distribution of these higher-grade results to refine target interpretations to support future programs and regional targeting efforts.
Table 1. Significant 2025 drilling results from Taurus Deposit based on a >0.4 g/t cutoff.
| Target Area | Drill Hole | From (m) |
To (m) |
Length* (m) |
Grade – uncapped (g/t Au) |
Grade – capped at 20 g/t (Au) |
|
| Taurus Southwest |
25TA-238 | 13.1 | 34.8 | 21.7 | 1.30 | – | |
| incl. | 13.1 | 21.2 | 8.1 | 2.18 | – | ||
| and | 33.2 | 34.1 | 0.9 | 5.11 | – | ||
| 101.4 | 112.6 | 11.3 | 1.21 | – | |||
| incl. | 101.4 | 102.0 | 0.6 | 8.33 | – | ||
| and | 106.8 | 107.6 | 0.8 | 7.38 | – | ||
| 129.8 | 130.2 | 0.4 | 6.67 | – | |||
| 148.9 | 149.8 | 0.9 | 27.18 | 9.63 | |||
| incl. | 148.9 | 149.3 | 0.4 | 59.50 | 20.00 | ||
| Taurus Central |
25TA-239 | 9.2 | 10.4 | 1.3 | 0.54 | – | |
| 32.8 | 34.8 | 2.0 | 7.56 | – | |||
| incl. | 32.8 | 33.2 | 0.4 | 19.55 | – | ||
| and | 34.0 | 34.8 | 0.8 | 9.14 | – | ||
| 92.6 | 112.2 | 19.6 | 0.58 | – | |||
| incl. | 92.6 | 94.5 | 1.9 | 2.09 | – | ||
| and | 102.9 | 103.4 | 0.5 | 4.01 | – | ||
| 25TA-241 | 71.7 | 73.5 | 1.8 | 0.78 | – | ||
| 130.5 | 131.8 | 1.3 | 1.69 | – | |||
| incl. | 130.5 | 131.0 | 0.4 | 3.25 | – | ||
| 164.4 | 166.1 | 1.7 | 3.15 | – | |||
| Sable | 25TA-240 | 8.9 | 10.6 | 1.7 | 4.83 | – | |
| incl. | 8.9 | 9.7 | 0.8 | 7.12 | – | ||
| 70.5 | 80.3 | 9.8 | 1.08 | – | |||
| incl. | 77.0 | 77.4 | 0.5 | 6.79 | – | ||
| and | 79.4 | 79.9 | 0.6 | 4.04 | – | ||
| 104.9 | 107.5 | 2.6 | 1.62 | – | |||
| incl. | 104.9 | 106.0 | 1.1 | 3.21 | – | ||
| 134.5 | 136.3 | 1.9 | 2.35 | – | |||
| 162.8 | 165.0 | 2.2 | 1.44 | – | |||
| incl. | 163.6 | 164.0 | 0.4 | 3.85 | – | ||
| 25TA-242 | 18.0 | 22.3 | 4.3 | 1.16 | – | ||
| 45.8 | 67.7 | 21.9 | 2.81 | 2.80 | |||
| incl. | 45.8 | 46.3 | 0.5 | 4.00 | – | ||
| and | 48.1 | 49.6 | 1.5 | 9.41 | – | ||
| and | 52.7 | 55.3 | 2.7 | 5.41 | – | ||
| with | 53.2 | 53.6 | 0.4 | 8.01 | – | ||
| and | 54.1 | 54.7 | 0.6 | 7.35 | – | ||
| incl. | 57.9 | 59.8 | 1.9 | 3.58 | – | ||
| and | 64.9 | 67.2 | 2.3 | 6.90 | 6.85 | ||
| with | 65.5 | 65.8 | 0.3 | 20.30 | 20.00 | ||
| 123.0 | 139.0 | 16.0 | 0.84 | – | |||
| incl. | 124.6 | 127.7 | 3.1 | 2.72 | – | ||
| with | 125.0 | 125.5 | 0.5 | 6.12 | – | ||
| 143.6 | 144.3 | 0.8 | 1.37 | – | |||
| 170.7 | 172.0 | 1.3 | 3.50 | – | |||
| Taurus East |
25TA-243 | 61.2 | 64.8 | 3.6 | 1.48 | – | |
| incl. | 61.2 | 61.7 | 0.5 | 7.08 | – | ||
| 114.0 | 114.5 | 0.5 | 3.77 | – | |||
| 25TA-244 | 35.2 | 35.7 | 0.5 | 2.96 | – | ||
| 59.4 | 60.3 | 0.9 | 1.67 | – | |||
| 88.4 | 115.7 | 27.3 | 0.65 | – | |||
| incl. | 89.5 | 90.6 | 1.1 | 4.42 | – | ||
| with | 90.0 | 90.6 | 0.6 | 6.01 | – | ||
| 25TA-245 | 28.2 | 41.6 | 13.4 | 13.53 | 2.05 | ||
| incl. | 29.0 | 29.3 | 0.3 | 56.10 | 20.00 | ||
| and | 39.8 | 40.6 | 0.8 | 210.71 | 20.00 | ||
| with | 39.8 | 40.2 | 0.4 | 369.00 | 20.00 | ||
| 56.5 | 76.0 | 19.6 | 0.42 | – | |||
| 90.0 | 95.0 | 5.0 | 2.00 | – | |||
| incl. | 94.2 | 94.6 | 0.4 | 15.00 | – | ||
| 130.0 | 131.0 | 1.0 | 1.31 | – | |||
| 25TA-246 | 88.4 | 89.4 | 0.9 | 1.09 | – | ||
| * Drill core lengths are reported here. True widths for these intervals have not been established | |||||||
Options
On December 2, 2025, the Company granted 2,270,000 stock options (the ‘Options’) to certain directors, officers, employees and consultants of the Company pursuant to its 10% rolling share option plan (‘Stock Option Plan’). The Options will vest with 2/3 of the Options vesting in 12 months from the date of grant, and the remaining 1/3 of the Options vesting in 24 months from the date of grant, at an exercise price of the Options will be $0.29.
Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC)
The 2025 Cassiar drilling program comprises HQ diamond drill core. Drill core samples are selected and logged by geologists prior to being cut in half using a diamond cutting saw at a secure facility located in Jade City, British Columbia. Certified gold reference standards and blanks are routinely inserted into the sample stream as part of the Company’s QA/QC program. All samples are delivered to the ALS Global preparation facility in Whitehorse, Yukon, then shipped to ALS Global preparation and analytical facilities in Vancouver, British Columbia. Samples are analyzed for gold by 50-gram fire assay with finish by atomic absorption or gravimetric methods. Screen metallic analysis is performed on selected samples. ALS Global quality systems and technical aspects conform to requirements of ISO/IEC Standard 17025 guidelines.
About Cassiar Gold Corp.
Cassiar Gold Corp. is a Canadian gold exploration company holding a 100% interest in its flagship Cassiar Gold Property located in British Columbia, Canada. The Cassiar Gold property spans 590 km2 and consists of two main project areas:
- Cassiar North, which hosts an updated Mineral Resource Estimate (MRE) for the Taurus deposit prepared in accordance with the Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum Definition Standards incorporated by reference in NI 43-101. The pit-constrained MRE contains Indicated Mineral Resources of 8.8 million tonnes (Mt) at 1.43 grams per tonne gold (g/t Au) for 410,000 ounces of gold in addition to Inferred Mineral Resources of 63.2 Mt at 0.95 g/t Au for 1.93 million ounces (Moz) of gold using a 0.4 g/t Au cut-off grade; 91% of ounces occur within 150 m of surface (see NI 43-101 Technical Report titled ‘National Instrument 43-101 Technical Report on the Cassiar Gold Property’, prepared by Zelligan, P.Geo, and Jolette, P.Geo, and dated effective June 8, 2025).; and
- Cassiar South, which hosts numerous gold showings, historical workings, and exploration prospects. Historical underground mines in the Cassiar South area have yielded over 315,000 oz of Au at average head grades of between 10 and 20 g/t Au (NI 43-101 Technical Report titled ‘National Instrument 43-101 Technical Report on the Cassiar Gold Property’, prepared by Zelligan, P.Geo, and Jolette, P.Geo, and dated effective June 8, 2025), underscoring the high potential for further discovery and expansion of high-grade orogenic gold veins.
The Company also holds a 100% interest in properties covering most of the Sheep Creek gold camp located near Salmo, British Columbia, Canada. The Sheep Creek gold district ranks as the third largest past-producing orogenic gold district in British Columbia from 1900 to 1951. Minimal exploration work has been conducted since the 1950s.
Qualified Persons
Jill Maxwell, P.Geo., Cassiar Gold Corp.’s VP Exploration, who is a Qualified Person as defined by National Instrument 43-101 has verified and approved the technical information in this press release.
Cassiar Gold Corp. acknowledges, respects, and supports the rights of Traditional First Nations in the lands and communities where we operate.
CONTACT INFORMATION
Jason Shepherd
VP Investor Relations
Cassiar Gold Corp.
E-mail: jasons@cassiargold.com
Phone: 250-212-2122
Forward-Looking Statements
This press release may contain forward-looking statements including those describing Cassiar Gold’s future plans and the expectations of management that a stated result or condition will occur. Any statement addressing future events or conditions necessarily involves inherent risk and uncertainty. Actual results can differ materially from those anticipated by management at the time of writing due to many factors, the majority of which are beyond the control of Cassiar Gold and its management. In particular, this news release contains forward-looking statements pertaining, directly or indirectly, to: timing and extent of planned drilling, potential for new discoveries, timing for providing assay results, conceptual areas for extension and expansion, size of the 2025 drill campaign, results from drilling and the risks and assumptions set out in the NI 43-101 Report.
Although Cassiar Gold believes that the expectations and assumptions on which the forward-looking statements are based are reasonable, undue reliance should not be placed on the forward-looking statements because the Company can give no assurance that they will prove to be correct. Since forward-looking statements address future events and conditions, by their very nature they involve inherent risks and uncertainties, actual results could differ materially from those currently anticipated due to a number of factors and risks. These include, but are not limited to, general economic, market or business conditions, risks associated with the exploration and development industry in general (e.g., operational risks in development, exploration and production; the uncertainty of mineral resource estimates; the uncertainty of estimates and projections relating to production, costs and expenses, and health, safety and environmental risks), constraint in the availability of services, commodity price and exchange rate fluctuations, a pandemic, changes in legislation impacting the mining industry, adverse weather conditions and uncertainties resulting from potential delays or changes in plans with respect to exploration or development projects or capital expenditures.
Readers are cautioned that the foregoing list of risk factors should not be construed as exhaustive. These statements speak only as of the date of this release or as of the date specified in the documents accompanying this release, as the case may be. The Company undertakes no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements except as expressly required by applicable securities laws.
Neither the TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release.
‘National Instrument 43-101 Technical Report on the Cassiar Gold Property’ by Zelligan, P.Geo, and Jolette, P.Geo.

To view the source version of this press release, please visit https://www.newsfilecorp.com/release/276754

News Provided by Newsfile via QuoteMedia