Experienced Thermal Integration Specialist Team Adds Depth to Syntholene’s Construction and Operational Roster
Syntholene Energy CORP (TSXV: ESAF,OTC:SYNTF) (FSE: 3DD0) (OTCQB: SYNTF) (‘Syntholene’ or the ‘Company’) announces that it has selected Papadakis Engineering (‘Papadakis’), the advanced fabrication and systems division of Papadakis Racing, as its development and integration partner for the geothermal heat exchanger system supporting Syntholene’s planned thermal-hybrid synthetic fuel Demonstration Facility.
Papadakis Engineering is a U.S.-based engineering and fabrication firm with deep expertise in high-performance thermal systems, precision manufacturing, and complex system integration.
The Papadakis organization is internationally recognized for its championship-winning motorsports engineering program, having designed and built record-setting powertrains and vehicle systems for top-tier professional racing series, including multiple Formula Drift titles.
The firm is known for translating extreme performance requirements into reliable, precision-engineered systems operating under continuous thermal and mechanical stress, a pedigree that directly informs its approach to advanced industrial thermal and integration challenges.
‘Thermal integration is one of the most important levers for Syntholene’s vision of lowering the cost of electrolytic hydrogen and, by extension, synthetic fuels,’ said Dan Sutton, Chief Executive Officer of Syntholene Energy Corp. ‘Papadakis brings an uncommon combination of thermal engineering, fabrication discipline, and execution speed. Their experience delivering tightly integrated, high-performance systems makes them an ideal partner as Syntholene moves from design into physical system validation.‘
The Company’s engagement of Papadakis is pursuant to a written project proposal dated January 28, 2026. The project scope covers detailed engineering, fabrication, containerized integration, and electrical scope associated with a geothermal heat exchanger skid designed to provide low-grade process heat to Syntholene’s Solid Oxide Electrolyzer Cell (SOEC)-based hydrogen production system. Under the proposal, Papadakis has agreed to provide electrical and heat exchanger integration services for a total contract value of US$289,026 payable in tranches during the term, with delivery of services expected to be complete by June 1, 2026. The work is intended to support factory acceptance testing and delivery of a fully integrated demonstration-scale system. This proposal was entered into by the Company in the ordinary course of its business in furtherance of the previously announced proposed Demonstration Facility. Papadakis and the Company are arm’s length parties.
‘Syntholene’s proposed Demonstration Facility represents the kind of engineering challenge we’re built for: integrating complex subsystems into a cohesive, performance-driven platform,‘ said Stephan Papadakis, Founder of Papadakis Engineering. ‘My team is excited to apply our high-performance engineering discipline to a program aimed at improving the efficiency and economics of synthetic fuel production.’
The selection of Papadakis represents a key milestone in the execution of Syntholene’s thermal-hybrid production architecture, which aims to integrate electricity with process heat to reduce net electrical demand and improve overall SOEC system efficiency. The proposed Demonstration Facility is designed to validate this approach and to generate operating data required to inform future commercial deployment plans.
The proposed Demonstration Facility is intended to serve as a validation platform for Syntholene’s thermal-hybrid production system, enabling the Company to de-risk system integration, operating performance, and unit economics ahead of targeted future commercial scale-up. Data to be generated from the facility is expected to inform subsequent project development, engagement with strategic partners, and discussions with policymakers and capital providers.
About Papadakis Engineering
Papadakis Engineering is an agile engineering, procurement, and construction firm specializing in advanced design, prototyping, precision fabrication, and integrated system development. The company bridges the gap between engineering and execution, enabling clients to move efficiently from concept through validated hardware.
Papadakis Engineering has deep experience solving complex mechanical, thermal, and electrical integration challenges under compressed timelines and high-performance requirements. Originally founded by champion Stephan Papadakis in the high-performance environment of professional motorsport, the firm applies that same discipline to industrial, energy, and advanced technology programs requiring precision, reliability, and secure operations.
About Syntholene Energy Corp
Syntholene is actively commercializing its novel Hybrid Thermal Production System for low-cost clean fuel synthesis. The target output is ultrapure synthetic jet fuel, which the Company seeks to manufacture at 70% lower cost than the nearest competing technology today. The Company’s mission is to deliver the world’s first truly high-performance, low-cost, and carbon-neutral synthetic fuel at an industrial scale, unlocking the potential to produce clean synthetic fuel at lower cost than fossil fuels, for the first time.
Founded by experienced operators across advanced energy infrastructure, nuclear technology, low-emissions steel refining, process engineering, and capital markets, Syntholene aims to be the first team to deliver a scalable modular production platform for cost-competitive synthetic fuel, thus accelerating the commercialization of carbon-neutral eFuels across global markets.
For further information, please contact:
Dan Sutton, CEO
comms@syntholene.com
www.syntholene.com
+1 608-305-4835
X: @Syntholene
Linkedin: Syntholene Energy
Youtube: Syntholene Energy
Investor Relations
KIN Communications Inc.
604-684-6730
ESAF@kincommunications.com
Neither TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release.
Forward-Looking Statements
This press release contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of applicable securities laws. The use of any of the words ‘expect’, ‘anticipate’, ‘aims’, ‘continue’, ‘estimate’, ‘objective’, ‘may’, ‘will’, ‘project’, ‘should’, ‘believe’, ‘plans’, ‘intends’, ‘targets’ and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking information or statements. All statements, other than statements of historical fact, including but not limited to statements regarding the proposal with Papadakis and proposed services, the timeline and cost for service delivery pursuant to the Papadakis proposal, proposed Demonstration Facility, testing planned at the proposed Demonstration Facility and the proposed use of data from such testing, commercial scalability,proposed benefits to the project from the skills of the engaged service providers, economic benefits of the Company’s products relative to competitive products; protection of the Company’s intellectual property through provisional patents and patents; the Company’s ability to execute on its plans for advancement and commercialization of its technology; technical and economic viability, anticipated geothermal power availability, anticipated benefit of eFuel, and future commercial opportunities, are forward-looking statements.
The forward-looking statements and information are based on certain key expectations and assumptions made by the Company, including without limitation the assumption that the Company will be able to execute its business plan in the manner and timeline set forth in its public disclosure or at all, that the engaged service providers have the skills to advance the Company’s business plans, that Papadakis will be able to complete the propsal on time and budget, that the eFuel will have its expected benefits, that there will be market adoption, that the Company’s review of the competitive landscape and that its understanding of being the world’s first Company to have geothermal-SOEC integration remain accurate, that any potential competitors to the Company would not be able to develop or execute geothermal-SOEC integration as quickly or as well as the Company, that the Company will be able to produce the eFuel at competitive pricing in the range anticipated in this news release or at all, that the proposed validation testing will be able to be completed, and that the results from such tests will validate the Company’s technology and support further commercialization, that geothermal heat will be available to the Company at the necessary levels, that the proposed Demonstration Facility will be completed on time and on budget, that the Company will continue to have access to skilled personnel with relevant experience, that regulatory requirements remain favourable for the Company, and that the Company will be able to access financing as needed to fund its business plan. Although the Company believes that the expectations and assumptions on which such forward-looking statements and information are based are reasonable, undue reliance should not be placed on the forward-looking statements and information because the Company can give no assurance that they will prove to be correct. Since forward-looking statements and information address future events and conditions, by their very nature, they involve inherent risks and uncertainties.
Actual results could differ materially from those currently anticipated due to a number of factors and risks, including, without limitation, Syntholene’s ability to complete the testing, that the results of the testing will support continued commercialization and the Company’s technology, that the engaged service providers do not have the necessary skills to and do not advance the Company’s business plan, that Papadakis is not able to complete the scope of services on time and on budget or at all, that there are competitors in geothermal-SOEC integration that are unknown to the Company, that the Company may not be able to produce eFuel at the targeted prices or at a price that is lower than potential competitors, that definitive commercial purchase orders for Syntholene’s eFuel may not materialize, Syntholene’s ability to meet production targets, realize projected economic benefits, overcome technical challenges, secure financing, maintain regulatory compliance, manage geopolitical risks, and successfully negotiate definitive terms. Syntholene does not undertake any obligation to update or revise these forward-looking statements, except as required by applicable securities laws.
This news release contains future-oriented financial information and financial outlook information (collectively, ‘FOFI’) about the cost and pricing of the eFuel product that Syntholene is seeking to commercialize, which is subject to the same assumptions, risk factors, limitations, and qualifications as set forth in the above paragraphs. FOFI contained in this news release was made as of the date hereof and was provided for the purpose of describing the anticipated effects of advancement of Syntholene’s business operations. Syntholene’s actual results, performance or achievement could differ materially from those expressed in, or implied by, such FOFI. Syntholene disclaims any intention or obligation to update or revise any FOFI contained in this news release, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, unless required pursuant to applicable law. Readers are cautioned that the FOFI contained herein should not be used for purposes other than for which it is disclosed herein.
Readers are advised to exercise caution and not to place undue reliance on the forward-looking statements and FOFI in this news release.

To view the source version of this press release, please visit https://www.newsfilecorp.com/release/288190













 technology, which uses high-energy X-ray excitation with gamma detection to quickly and non-destructively measure gold content.
technology, which uses high-energy X-ray excitation with gamma detection to quickly and non-destructively measure gold content.








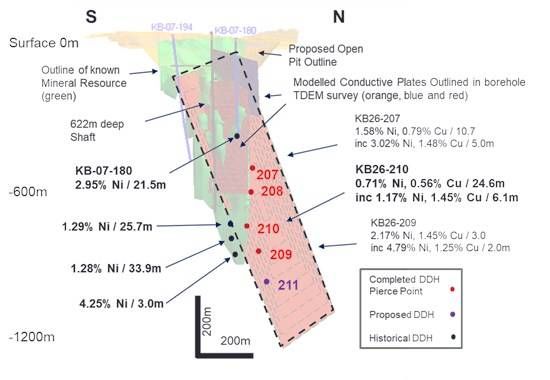
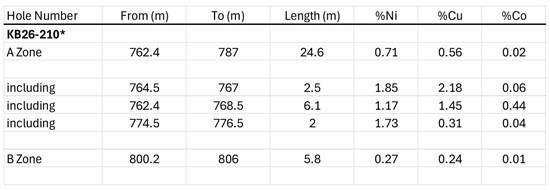
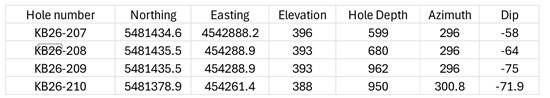





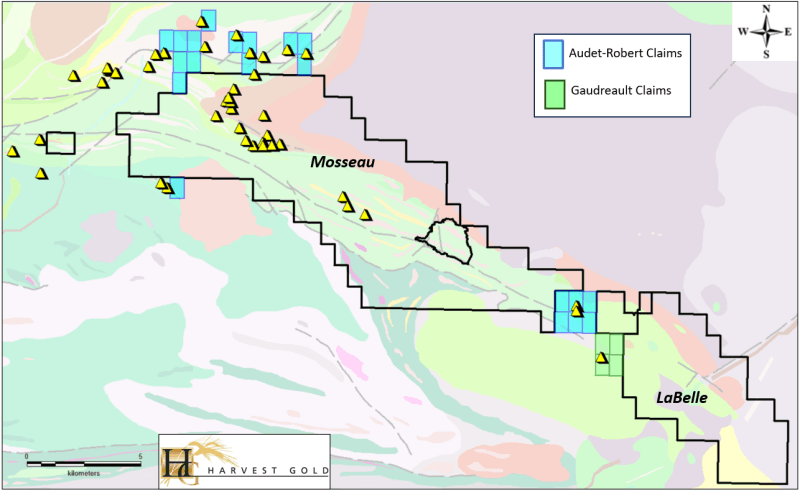













 Red Mountain Mining Limited (ASX: RMX, US CODE: RMXFF, or “Company”) a Critical Minerals exploration and development company with an established portfolio in Tier-1 Mining Districts in the United States and Australia, is pleased to announce that it has received continued strong assay results from the second tranche of assays for its auger soil sampling program at the Oaky Creek prospect at the Company’s 100% owned Armidale Antimony-Gold project in New South Wales.
Red Mountain Mining Limited (ASX: RMX, US CODE: RMXFF, or “Company”) a Critical Minerals exploration and development company with an established portfolio in Tier-1 Mining Districts in the United States and Australia, is pleased to announce that it has received continued strong assay results from the second tranche of assays for its auger soil sampling program at the Oaky Creek prospect at the Company’s 100% owned Armidale Antimony-Gold project in New South Wales.