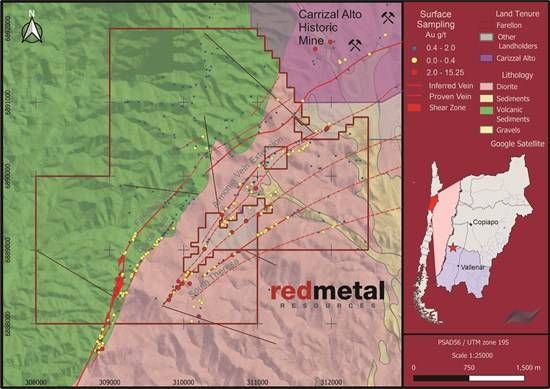
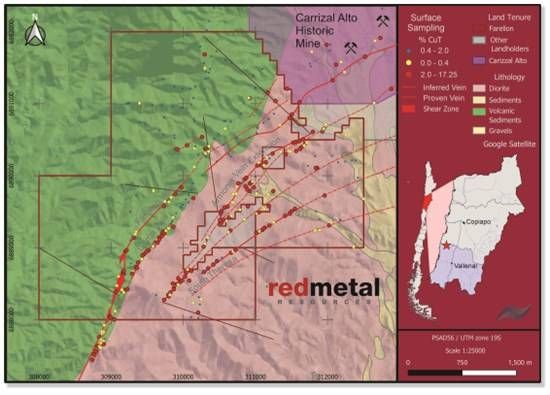
TSXV: DMCU; OTCQB: DMCUF; FSE: 03E0) engages TMC Geophysics to conduct 27 line-kilometers of electrical geophysics (Induced Polarization; ‘IP’) at the Smart Creek Project, Montana. The geophysical program is designed to expand historical IP coverage on the property and will be used to refine the location of diamond drilling scheduled for Q1Q2, 2026. IP geophysics is used to obtain chargeability and resistivity values (rock properties) which can provide insights into the distribution of sulphides and hydrothermal alteration related to potential porphyry and Carbonate Replacement deposits in the subsurface at Smart Creek and will be used by Domestic to derisk drill targets in advance of drilling.
Domestic Metals has expanded its exploration budget significantly to accommodate additional geophysics and diamond drilling at Smart Creek based on results of the 2025 surface sampling program that substantially increased the mineralized footprint of existing targets at Smart Creek and identified several new targets for follow up exploration (see news release dated January 8, 2026). The 2025 sampling program returned the following high-grade results:
Highlight High-Grade Assay Results
- 102 g/t Au (Sample G019007)
- 74.7 g/t Au, 13.8% Cu, 3810 g/t Ag (Sample G019235)
- 30.4 g/t Au (Sample G019001)
- 26.6 g/t Au (Sample G019353)
- 23.1% Cu, 424 g/t Ag (Sample G019225)
- 19.65% Cu, 458 g/t Ag (Sample G019031)
- 19.05% Cu, 582 g/t Ag (Sample G019038)
Non-brokered Private Placement
Domestic Metals announces a non-brokered private placement of up to 12,500,000 units (the ‘Units’) at a price of $0.28 per Unit (the ‘Offering’) for gross proceeds of up to $3,500,000. Each Unit will consist of one common share of the Company (a ‘Share’) and one common share purchase warrant (a ‘Warrant’). Each whole Warrant entitles the holder to acquire one additional Share of the Company for a period of two years from the date of issuance at a price of $0.40 per Share. Expiry of the Warrants may be accelerated if the closing price of the Company’s Shares on the TSX Venture Exchange (‘TSXV’) is equal to or greater than $0.65 for a minimum of twenty consecutive trading days and a notice of acceleration is provided in accordance with the terms of the Warrants.
Gord Neal, CEO of Domestic Metals Corp. commented: ‘We expanded our exploration budget significantly to accommodate additional geophysics and up to 9,000m of diamond drilling at Smart Creek. This follows the discovery of high-grade mineralization, including up to 102 g/t gold, 23% copper, and 3,810 g/t silver we announced last month. These field campaign results generated significant unsolicited capital market interest making this private placement announcement timely. The geophysics program to be launched this week will refine drill targets for the larger diamond drill program scheduled to start in Q1, 2026.’
Insiders may participate and finders’ fees may be payable to qualified arm’s length parties that have introduced the Company to certain subscribers participating in the Offering. All securities issued in the Offering are subject to a four-month hold period, during which time the securities may not be traded. Closing of the Offering is subject to the approval of the TSXV.
The net proceeds from the Offering are intended for exploration of the Company’s Smart Creek Project, in Montana, U.S.A., and for general working capital.
This press release does not constitute an offer of sale of any of the foregoing securities in the United States. None of the foregoing securities have been and will not be registered under the U.S. Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the ‘1933 Act’) or any applicable state securities laws and may not be offered or sold in the United States or to, or for the account or benefit of, U.S. persons (as defined in Regulation S under the 1933 Act) or persons in the United States absent registration or an applicable exemption from such registration requirements. This press release does not constitute an offer to sell or the solicitation of an offer to buy nor will there be any sale of the foregoing securities in any jurisdiction in which such offer, solicitation or sale would be unlawful.
Opportunity to Meet with Domestic’s Management
We appreciate meeting with our supporters and shareholders in person to provide a detailed update and as such are looking forward to seeing you at our booth #3139 at the Investors Exchange at the PDAC, March 1-4, 2026, in Toronto.
Technical Information
All scientific and technical information in this news release has been reviewed and approved by Daniel MacNeil, P.Geo. Mr. MacNeil is a Technical Advisor to the Company and is a qualified person for the purposes of National Instrument 43-101 – Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects.
About Domestic Metals Corp.
Domestic Metals Corp. is a mineral exploration company focused on the discovery of large-scale, copper and gold deposits in exceptional, historical mining project areas in the Americas.
The Company aims to discover new economic mineral deposits in historical mining districts that have seen exploration in geologically attractive mining jurisdictions, where economically favorable grades have been indicated by historic drilling and outcrop sampling.
The Smart Creek Project is strategically located in the mining-friendly state of Montana, containing widespread copper mineralization at surface and hosts 4 attractive porphyry copper, epithermal gold, replacement and exotic copper exploration targets with excellent host rocks for mineral deposition.
Domestic Metals Corp. is led by an experienced management team and an accomplished technical team, with successful track records in mine discovery, mining development and financing.
On behalf of Domestic Metals Corp.
Gord Neal, CEO and Director
(604) 657 7813
Follow us on:
X, LinkedIn, Facebook and Instagram
For more information on Domestic Metals, please contact:
Gord Neal, Phone: (604) 657 7813 or Michael Pound, Phone: (604) 363 2885
Please visit the Company website at www.domesticmetals.com or contact us at info@domesticmetals.com.
For all investor relations inquiries, please contact:
John Liviakis, Liviakis Financial Communications Inc., Phone: +1 415 389 4670.
Neither TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release.
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
This news release contains certain statements that may be deemed ‘forward-looking statements’. Forward-looking statements are statements that are not historical facts and are generally, but not always, identified by the words ‘expects’, ‘plans’, ‘anticipates’, ‘believes’, ‘intends’, ‘estimates’, ‘projects’, ‘potential’ and similar expressions, or that events or conditions ‘will’, ‘would’, ‘may’, ‘could’ or ‘should’ occur. Forward-looking statements may include, without limitation, statements relating to the Offering and the planned exploration activities on properties. Although the Company believes the expectations expressed in such forward-looking statements are based on reasonable assumptions, such statements are not guarantees of future performance, are subject to risks and uncertainties, and actual results or realities may differ materially from those in the forward-looking statements. Such material risks and uncertainties include, but are not limited to: competition within the industry; actual results of current exploration activities; environmental risks; changes in project parameters as plans continue to be refined; future price of commodities; failure of equipment or processes to operate as anticipated; accidents, and other risks of the mining industry; delays in obtaining approvals or financing; risks related to indebtedness and the service of such indebtedness; as well as those factors, risks and uncertainties identified and reported in the Company’s public filings under the Company’s SEDAR+ profile at www.sedarplus.ca. Although the Company has attempted to identify important factors that could cause actual actions, events or results to differ materially from those described in forward-looking information, there may be other factors that cause actions, events or results not to be as anticipated, estimated or intended. Accordingly, readers should not place undue reliance on forward-looking statements. There can be no assurance that such information will prove to be accurate as actual results and future events could differ materially from those anticipated in such statements. Forward-looking statements are made as of the date hereof and, accordingly, are subject to change after such date. The Company disclaims any intention or obligation to update or revise any forward-looking information, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise unless required by law.